In a series circuit with R, L, and C, the applied voltage U is equal to the sum of the voltage drops across the resistor, inductor, and capacitor. We can find it

Specify the impedance of the circuit through the following methods:
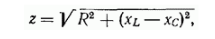
We can write Ohm's law for this circuit:
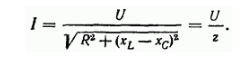
In the considered circuit, when the load is an active inductor and an active capacitor.
So what is the current in the circuit
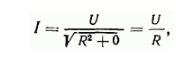
That is, in this case, the circuit has the smallest possible resistance, as if it only contains active resistors. In this case, the voltages on the phase of the inductor and capacitor completely cancel each other out. The voltage applied to the circuit is equal to the voltage across the active resistor, and the current is in phase with the voltage. This situation is called series resonance (also known as variable frequency series resonance).
Therefore, the condition for series resonance is that the inductance, capacitance, and resistance of the circuit are equal:
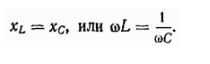
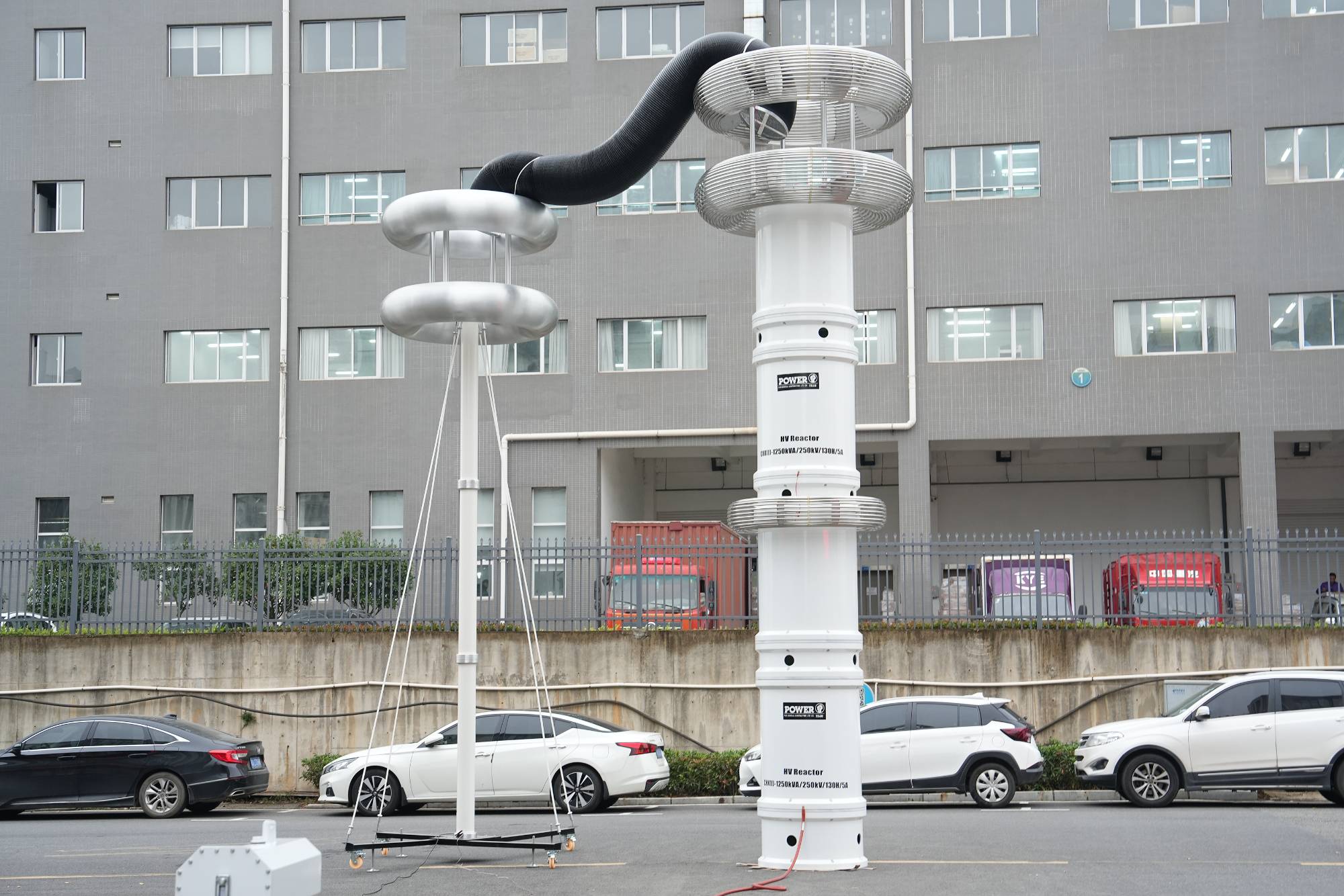
The phenomenon of series resonance is important for practice.
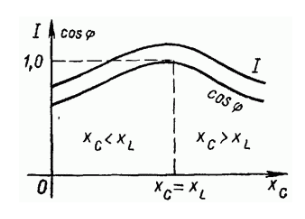
Firstly, if a variable capacitor is connected in series with an inductor and gradually changed, such as increasing it, the current in the circuit will first increase until resonance occurs, and then decrease. Introducing capacitors into a circuit to reduce its reactance is called sequential compensation. When the result is insufficient compensation, overcompensation, and complete compensation (when the current reaches its maximum, a). This compensation method is sometimes used in practice to increase the network. Vertical (sequential) compensation is used, for example, in transmission lines.
Additionally, if we use the ratio of applied voltage to voltage
Inductance (or capacitance) part:
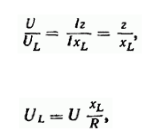
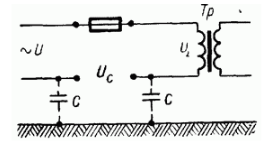
That is, when the voltage on the reactive part is greater than the applied time. This means that with the series resonance of certain parts in the circuit, voltage may occur, which is dangerous for isolating the windings of the equipment and machines contained in this circuit. For example, when series resonance occurs, the induced voltage on the transformer winding may be significantly higher than the voltage designed for the winding itself, resulting in insulation damage.
However, series resonance is not only a bad phenomenon that must be considered when calculating power circuits, but also very useful. Specifically, in wireless engineering resonant circuits, due to series resonance, significant amplification of weak wireless signals is achieved by forming high voltages on capacitors and inductors. Therefore, the inductance and resistance of the circuit are many times greater than its active resistance